The Different Capacitor Types: Symbols and Applications
February 7, 2023

Here, we will discuss the different capacitor types used in electronics today.
Capacitors play a significant role in a wide range of electrical applications. A common use of this component is in power supply circuits. They store electrical energy and then release it back when needed by the circuit.
But beyond that, many have no idea what else capacitors are capable of or why they are essential. If you want to learn more about their basic properties, keep reading. This post will cover their purpose and how they work, as well as the different capacitor types.
Defining Capacitors
Capacitors are regarded as passive components due to their lack of power sources. They are made up of two conductors separated by dielectric material.
Their working principle is simple: to store and release energy. Say a voltage is applied across the terminals of the capacitor. What it does is it accumulates a charge and saves energy into an electrical field. This effect is known as capacitance.
The points of contact between the two conductors are the ‘plates’. The plate can be in the form of aluminium foil, paper, or plastics like polypropylene. In a capacitor, there are two plates. One collects the positive charge, and another gathers the negative.
The capacity depends on the size of the capacitor and the dielectric. The higher it is, the larger the plates with more surface area and a higher relative permittivity. This is usually measured in Farads (F), where one Farad equals 1 Coulomb per Voltage (1F 1C/V).
Capacitors also vary on the following:
- Maximum operating temperature
- Leakage current
- Ability to handle high-frequency signals
Symbols
The symbol for capacitors consists of two parallel lines, which are either flat or curved. Both lines should be parallel-closed to each other but not touching.
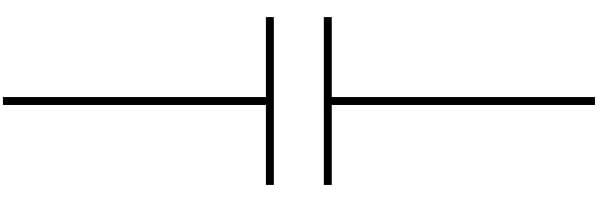
Capacitance is the ratio of electric charge (Q) to voltage (V). The mathematical expansion for this is C = Q/V. Where,
- Q is the electric charge in coulombs
- C is the capacitance in farad
- V is the voltage between the plates in volts
Availability
Capacitors come in many shapes and sizes, from tiny disc models to large power generators. They can be found anywhere there is electricity involved. This includes applications like:
- Filters and oscillators in audio electronics
- Motors, relays and magnets in power controls
- Timing circuits
Today, capacitors are even used for advanced energy storage systems like hybrid cars. The same goes for gadgets, e.g. smartphones, that need rapid charging.
Polarisation
Capacitors are classified into two types according to polarisation: polarised and unpolarised.
Polarised
A polarised capacitor achieves high capacitive density. The term ‘polarised’ refers to the positive-negative charge within the capacitor.
Polarised capacitors are important in many electrical circuits. Their ability to store potential energy while controlling current flow is a factor.
They also provide help signalling circuit protection against high voltage damage. Plus, to prevent transients from passing through power supplies too quickly. This protects equipment from costly damage or failure, in turn.
A polarised capacitor is ideal for use in one voltage direction.
Unpolarised
An unpolarised capacitor has no implicit polarity, but it connects in circuits – both AC and DC. Unlike its polarised counterpart, it does not have positive and negative ends.
Moreover, its frequency is high, while the leakage current is low. They are often used in circuits of coupling, decoupling, feedback, compensation, and oscillation.
Unpolarised capacitors are ideal for use in both voltage directions.
Different Capacitor Types
Capacitors are categorised into two mechanical groups: fixed and variable. Fixed capacitors consist of a fixed capacitance value; variable with a variable capacitance value.
When it comes to capacitor types, there are a few, which you can browse through below, including their uses:
Ceramic capacitors
A ceramic capacitor is one of the most often used capacitors. It is a non-polar device, making it ideal for use in any direction of the circuit. The material used is dielectric.
Other applications include:
- In printed circuit boards used in high-density applications
- DC motors for reducing RF noise
- Transmitter stations where resonant circuits are present
Film capacitors
A film capacitor, also known as a polymer film, comes with limitless shelf life. It uses a thin dielectric material with the other side metallised.
Depending on the application, it can be rolled into thin films to add. The general voltage range of this type of capacitor is from 50V to 2kV.
Common applications of film capacitors include:
- In electromagnetic interference as safety capacitors
- Power Electronics
- To safeguard devices from sudden voltage spikes
Paper capacitors
A paper capacitor consists of dielectric material that is paper, hence the name. It holds a specific quantity of electric charge. As a result, it is classified as a “fixed capacitor” type.
Two types of paper are used in this type of capacitor: paper sheet and metallised paper. Applications of paper capacitors are as follows:
- In noise filtering, coupling, and decoupling systems
- Blocking the DC signals to enable AC signals to pass through
- Sensors such as humidity sensors and fuel level sensors
- In car audio systems to provide extra power to the amplifiers
Electrolytic capacitors
An electrolytic capacitor uses an electrolyte to achieve a larger capacitance. It consists of a liquid or gel with a high concentration of ions.
Most electrolytic capacitors are polarised. This means the voltage on the positive terminal is greater than on the negative. They are commonly used:
- When there is a requirement for large capacitance
- As filtering devices that lower the ripple voltage
- In audio amplifiers to reduce the electrical noise induced by the main supply
- In smoothing the input and output signals in a DC signal that has a weak AC component
The Value
Depending on the capacitor types, the values vary. For instance, an electrolytic has its values printed on the body along with the pins. Some have theirs represented in PF, uF, KPF, and more. A black band is also used to show the negative terminal of the capacitor.
Get Your Capacitors Here!
Capacitors, also known as condensers, are energy-storage devices in most electronic equipment. Check out below our range of capacitors available in ceramic and electrolytic types:
Ceramic Capacitors
Ceramic capacitors in 50 and 500V, with a big range of capacitance values! Low inductance, suitable for RF use, filters, coupling, and decoupling applications. 50V ceramic capacitors are also available in a 60-pack of mixed values, so you can always have a variety on hand.

1. 50V Disc Ceramic Capacitors
These 50V disc ceramic capacitors feature low inductance and high capacitance per volume.

2. Ceramic Disc Capacitors 500V
These ceramic disc capacitors are low inductance. Suitable for RF use, filters, coupling, and decoupling applications.

3. Ceramic Capacitor Pack – 60 Pcs (Values from 10pF to 0.1uF)
Product code: JRC5399
Ceramic Capacitor Pack – 60 pieces. Top-quality prime spec 50V working ceramics. Values from 10pF to 0.1uF.
Electrolytic Capacitors
A range of electrolytic capacitors for just about any use! Also available in bags of mixed values, so you can conveniently keep a variety of capacitors on hand.

1. RB Electrolytic Capacitor – High Voltage
High-performance, high-voltage, general-purpose aluminium RB electrolytic capacitor, radial type.

2. Electrolytic Capacitors (RT) Axial (Double Ended)
These are general-purpose aluminium electrolytic capacitors, axial type (double-ended). Ideal for low-profile circuit board applications.

3. RB Electrolytic Capacitor – Low Voltage
High performance, low voltage, general-purpose aluminium RB electrolytic capacitor, radial type. Different capacitor values and voltages are available.

4. RB Electrolytic Capacitor Pack – 55 pcs (Values from 1μF to 470μF)
Product code: JRE6250
Pack of 55 pcs quality electrolytic capacitor, most RB types. Values range from 1μF to 470μF. Voltages from 16 to 63.

5. 47,000µF 40VDC Capacitor with Clamp
Product code: CC1860
High-performance aluminium electrolytic capacitor, durable and resistant to corrosion. Specifications include:
Capacitance tolerance
±20% at 100 Hz, 20°C [M class IEC-62]
DC leakage current (5 min, 20°C)
0.006 Cr Vr + 4 µA
The Bottom Line
Capacitors essentially act as small batteries that charge whenever voltage passes through them. But unlike batteries, they do not suffer diminished capacity over time. This is due to use or storage, whereas batteries tend to run out of charge after repeated usage.
By understanding capacitance and how these devices work, you can ensure optimal performance. Whether for simple appliances or advanced scientific equipment!
© Electrotech Brands Pty Ltd 2023


Write a Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.